This September, I’ll eagerly be scanning and listening for both migrating birds and rare species, as I do throughout the year. Indeed, I’m one of those individuals who can be spotted amidst a crowd, peering through a long scope at a distant bird.
In fact, last February, upon receiving a “Rare Bird Alert” on my phone about a rare eagle sighting in Maine, I jumped into my bird-mobile and drove 4.5-hours to catch a glimpse of it. It wasn’t until I arrived that I realized I had forgotten my coat. Nevertheless, there I was, trudging through muddy terrain in light fog, alongside a hundred other freezing fanatics from as far as Canada and the UK. Thankfully, we all succeeded in spotting the rare Stellar’s Sea Eagle, and it was truly magnificent!
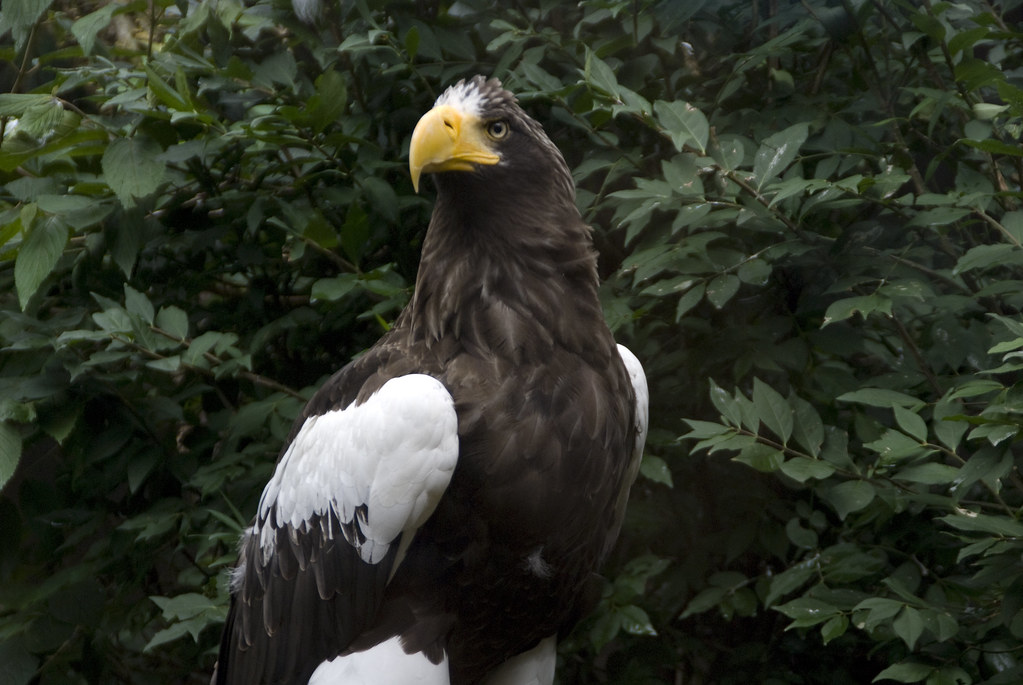

When people discover that I am a birder, they often express surprise, saying, “Wow, that’s so different from your day job at Unilever.”
But is it? Birding cultivates a range of skills that can be immensely valuable in industries and positions that demand innovation. Here are my top 10 reasons to consider adding a birder to your innovation team:
- Curiosity and Exploration: Birders possess an innate curiosity about the world around them and an inclination to explore and discover new things. This natural curiosity fuels their creativity and propels them to venture into uncharted territories within industries, leading to innovative ideas and approaches.
- Systems Thinking: Birding fosters an understanding of the interconnectedness of ecosystems and the intricate relationships between different bird species, plants, and habitats. This systems-thinking approach can be applied to industries that require innovation and technology, where comprehending the broader context and the interdependencies between various components is crucial for developing innovative solutions.
- Observational Skills: Birders excel at observation, which proves advantageous in numerous business contexts, such as consumer science, research, and market analysis. Their ability to perceive and interpret subtle details helps uncover consumer preferences, identify market trends, and understand customer behavior.
- Flexible Attention to Detail: To be a proficient birder, one must literally know when to focus on the forest vs. the trees. In the business context, this flexibility proves valuable for simultaneously grasping the overall context and delving into details when necessary.
- Pattern Recognition: Birdwatchers hone their pattern recognition skills by identifying various bird species based on visual and auditory cues. This acute eye for detail translates well into industries that necessitate meticulous observation and analysis, as innovation often entails identifying subtle patterns, trends, or opportunities that others may overlook.
- Decision Making: Birders frequently find themselves making prompt judgments based on incomplete data, a situation commonly encountered in the business world as well. Birders rely on their pattern recognition skills, allowing them to recognize familiar scenarios and make optimal decisions until further information becomes available.
- Listening Skills: The better a birder you are, the less you rely on sight and the more you rely on listening to calls to identify species. In the workplace, it is crucial to truly listen and understand others, rather than merely appearing attentive until one has a chance to speak. When people feel genuinely heard, it leads to better outcomes for all parties involved.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Birders frequently maintain records of their sightings, engage in field research, study bird behaviors, migration patterns, and habitat requirements. This experience in conducting research and gathering data proves valuable in industries that require innovation or research and development, where data-driven decision-making and evidence-based practices are essential.
- Sustainability Mindset: Many birdwatchers are passionate about preserving the Earth for future generations. This mindset can be relevant in industries where sustainability and environmental considerations are crucial aspects of innovation. Birdwatchers may bring a heightened awareness of ecological impact, leading to the development of innovative, eco-friendly practices or technologies.
- Collaboration and Networking: Birders regularly interact with other birdwatchers, scientists, and conservationists to share knowledge and collaborate on projects. This networking and collaborative mindset can be applied to innovation industries, where interdisciplinary teamwork and knowledge exchange can yield groundbreaking ideas.
Watch Innovation Soar
Although being a birdwatcher may not directly provide expertise in all areas of innovation, the skills and qualities developed through birdwatching contribute to a mindset conducive to creative problem-solving, adaptability, and a holistic approach to innovation. So consider becoming a birdwatcher or hiring one to be part of your team and watch as your innovation acumen soars!
Contributor
-

Gail Martino, Ph.D is a thought leader and global innovation leader in the fast-moving consumer goods industry, having worked with billion-dollar brands at Unilever and previously at Gillette. With a background spanning both corporate and academic roles, Gail has a proven track record in developing and executing highly effective innovation ecosystems, driving value through strategic partnerships and internal product development. Notably, she has been a valued member of the advisory board for the Front End of Innovation conference since 2015.
View all posts